

This paper addresses the problem of generating deterministic -automata for formulas of linear temporal logic, which can be solved by applying wellknown algorithms to construct a nondeterministic Bchi. It can accept any string which ends with 0 like 00, 10, 110, 100.etc. Safra’s determinization algorithm is studied in detail, several heuristics that attempt to decrease the size of the resulting automata are presented and experimental results are reported on. This paper gives a tableau-based technique for converting formulas in finite propositional linear-time temporal logic (Finite LTL) into finite-state automata whose languages are the models of the given formula. DFA does not accept the null move, i.e., the DFA cannot change state without any input character. Safra’s determinization algorithm is studied in detail, several heuristics that attempt to decrease the size of the resulting automata are presented and experimental results are reported on.
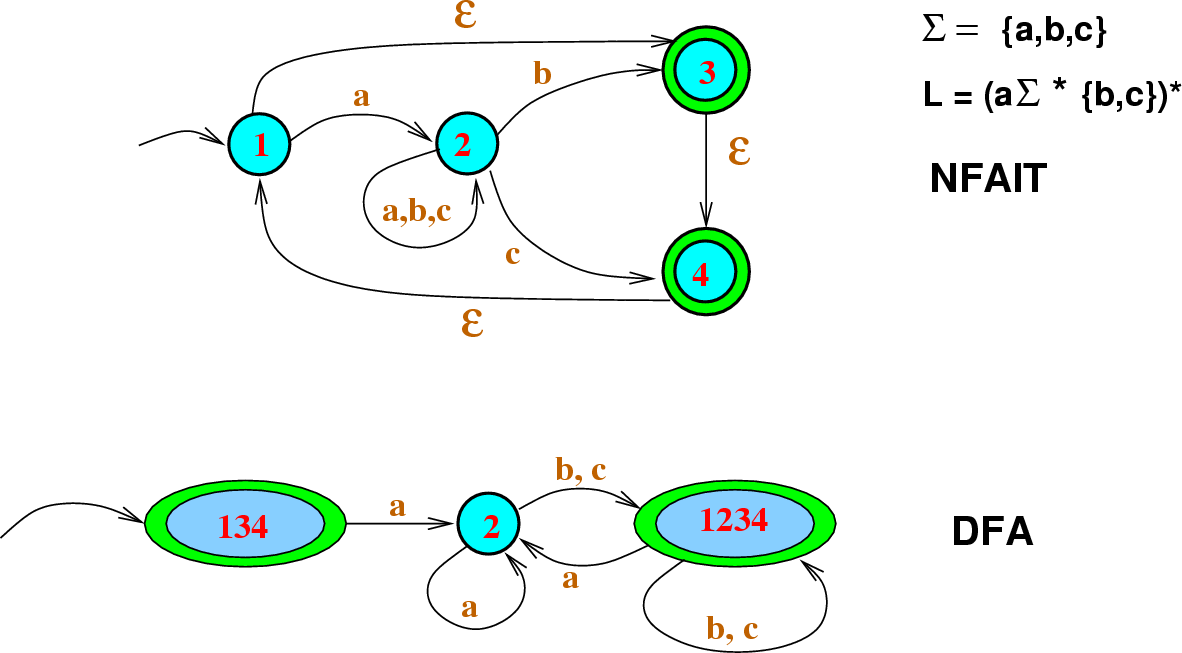
In DFA, there is only one path for specific input from the current state to the next state. One of the novelties is to translate LTL into a limit deterministic generalized Büchi automaton (LDGBA) and develop a corresponding embedded LDGBA (E-LDGBA) by. In the above diagram, we can see that on given 0 as input to DFA in state q0, the DFA changes state to q1. The finite automata are called deterministic finite automata if the machine is read an input string one symbol at a time. A model-free reinforcement learning (RL) is developed to generate a finite-memory control policy to satisfy high-level tasks expressed in linear temporal logic (LTL) formulas.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
